Ever since the Apple Watch series 3, which was first launched in 2017, the device has been reporting Apple on ‘Cardio Fitness’ or VO2 max. V02 max is a measurement of how much oxygen the body consumes during intense workouts and is used as a way to guage how fit you are.
Some Watch wearers use VO2 max as the alternate name suggests, to guage Cardio Fitness. If your increased cardio activity is making you more fit, the VO2 max should show this, assuming that Apple Vo2 max is accurate. But measuring the amount of oxygen you consume has to do with the lungs and heart, not your wrist. So how does a watch guage your fitness and how accurate is the VO2 max reading on the Apple Watch?
First we should highlight that the gold standard for measuring VO2 max are lab based tests that will require a mask covering your nose and mouth. This allows for analysis of the CO2 exhaled in order to calculate the volume of O2 being used.
This article summarizes how the watch based reading compares to a lab based treadmill test. The results were an estimated reading that had the Apple Watch overestimating VO2 max by about 6-8%, or +4.0 mL/kg/min, across three different testing periods.
In a single day of testing, wearing both an Apple Watch series 8, we tested VO2 max against the primary standard of a stress test. This is also compared to other performance apps that make an estimate of VO2 max using similar calculations that the Apple Watch uses.
- Apple Watch Series 8 VO2 Max estimate- 57.9 mL/kg/min
- DexaFit Treadmill & Mask Test Output- 53.9mL/kg/min
- Health Mate App estimate – 55
- Zwift VO2 Max estimate – 52.0
Results here are from a single person and Apple Watch, broader studies show similar results with a FitBit which also uses sub-maximal effort to predict VO2 max. The results of Fitbit “shows consistent, unbiased measurement of (Cardio Fitness Score) while overestimating VO2max in healthy men and women” (source). Again these results are from a small sample but suggest a pattern in the overall accuracy.
Apple Watches accuracy does have limitations. Outliers are tough to guage, for very fit individuals or those with low fitness the minimum (14 mL/kg/min) accuracy will vary widely.
There is no reason to believe that any particular series of Apple Watch will provide more accuracy. Apple does not release the exact equation used to calculate VO2 max, but it is known to be based on changes in HR.
And even though the watch can make an estimate from a submaximal effort the absolute accuracy is likely to improve as you do more efforts of varying intensity. This goes for all the apps making estimates. In our early days of riding on Zwift it was predicting well below other data points for VO2 max, with low 40s compared to Apple Watch at 52 mL/kg/min or more. After a hard 20min time trial and day with a 5min max power test the Zwfit VO2 estimates jumped to 52.0 mL/kg/min.
Understanding VO2 Max and Cardio Fitness – Measured by Apple Watch
Cardio fitness is NOT something that will change significantly from day to day. If you have monitored workouts for a while you may see however see spikes in Cardio Fitness. That is likely because the wrist worn, blood oxygen concentration monitoring watch uses a calculation to get a VO2 max result.
Other fitness measures, including the Strava fitness score and things like a Training Peaks Training Stress Score (TSS) measure a training load or how much activity you have actually done. In theory the metrics are tied together, but VO2 max is a more objective bodily measurement compared to “fitness”.
Spikes in average VO2 max are due to one of the major factors of the estimate being updated. This could include a new software release the changes the algorithm or an update to related variables (ie. updates or corrections to your tracked weight, age, etc.).
If the equation used to calculate VO2 changes, as it sometimes does during software updates in order to improve accuracy as the technology and science develop, you may see a spike. In 2020 and 2021 there were noticeable changes in VO2 max readings just after the watch updated. More recent watchOS updates, those in 2022 and 2023 did not have the same impact on our readings.
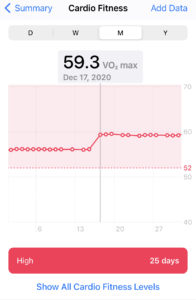
Without a software update, the accuracy of the watch is still pretty good. It’s unlikely to fluctuate day to day so trends over time are easy to spot. It is also important to understand that you will only get a VO2 max data point for uninterrupted 20+ minute outdoor workouts.
If you are doing treadmill running, or your HR sensor looses a reading, or if you pause an outdoor activity you will not see a new VO2 max data point.
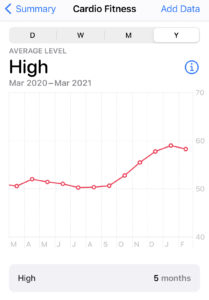
The image above show the trends of VO2 Max from a watch during a training cycle. Starting at 15-20 miles of running per week and moving up to 45-50 mile weeks over the course of a few months the trends are obvious.
DexaFit VO2 Max Accuracy
The term “accuracy” assumes you know the true measurement. DexaFit, like other wellness centers, uses a mask based monitoring system to read your true VO2 during a 10-20 minute hrs effort.
The duration of the test is based on performance, you can opt out on your own. During an initial test this might be at a sub maximum effort. Personally, running at full 12.5% incline on a treadmill, while wearing a mask that at least partially resists breathing in was abnormal. In the same way that you can train for a hard 5k effort it is possible to train for a VO2 max test simply but being familiar with the format.
On our tests the examiner agreed many people can perform better on a second test, a day or two later, just by knowing what to expect. Other situational cues, a coach cheering you on , a competitor on the treadmill next to you, good music, etc. all could have impact on the mental ability to push the test to the limit. For this reason it’s safe to assume that a single mask based VO2 max test is most likely to underestimate the true maximum.

If you manage to get to exhaustion, the peak is likely to be your max and . Having done the test, where my heart rate peaked (178bpm) about 7-8 beats below what I’ve observed during workouts (185bpm), it appears the treadmill DexaFit measurement aligns well with an Apple Watch prediction.
DexaFit Treadmill Test Experience
After a tough 13 minute effort on the treadmill the Dexafit test resulted in almost within a rounding error of Apple’s prediction from the same effort, suggesting that compared to a lab test the Apple Watch V02 max accuracy was spot on. Although there is not a 7% variability in day to day predictions from my the watch, there was no indication that either was fundamentally flawed as a measurement.
Since the treadmill is a one time thing (given the cost which was around $100), and my watch providing a nearly identical reading pretty much anytime I do a 30 minute run, the nod has to go to Apple for their VO2 max accuracy.
A secondary, and arguably primary, benefit to the treadmill test is to see when you pass through threshold levels. For heart rate training this is key. Below a factor of 1, your body is clearing lactic acid at a rate faster than its building up. Many training plans use “Zone 2” style running or riding to build a baseline of fitness.
This is the threshold at which burning starts accumulating in muscles, since lactate build up is what casuses the burn in muscle. In endurance athletics keeping this heart rate in mind is the difference between hitting the wall and finishing strong, and is a level that is easier to recover from in training.
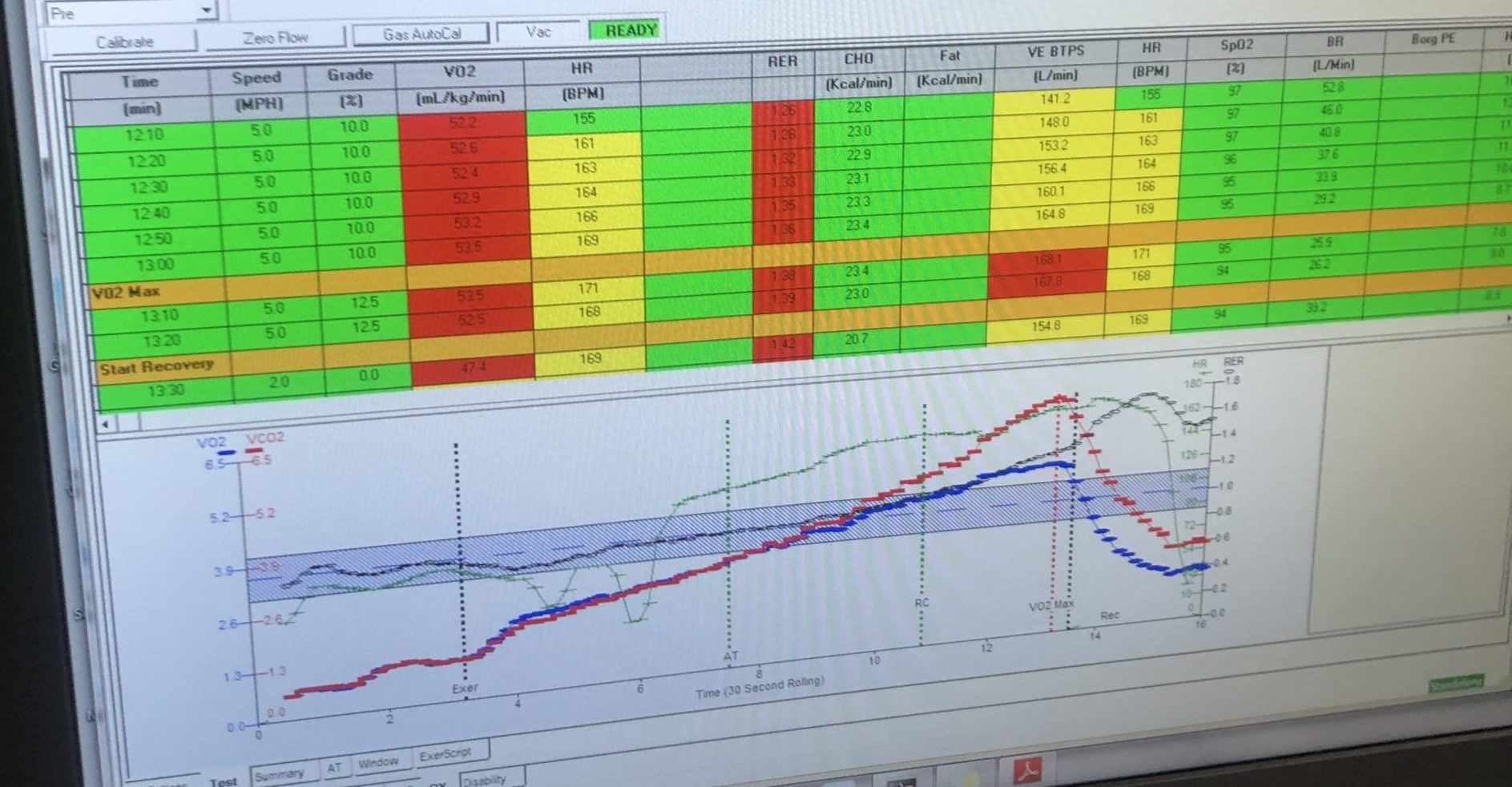
Because the treadmill test starts at a warmup and escalates to max effort, you can monitor these zones of lactate build up. This again is something that can be estimated by calculators, and you can set your watch to alert you at different zones, but this is a personalized measure and knowing your own body can help make the small differences that the calculators will not enable.
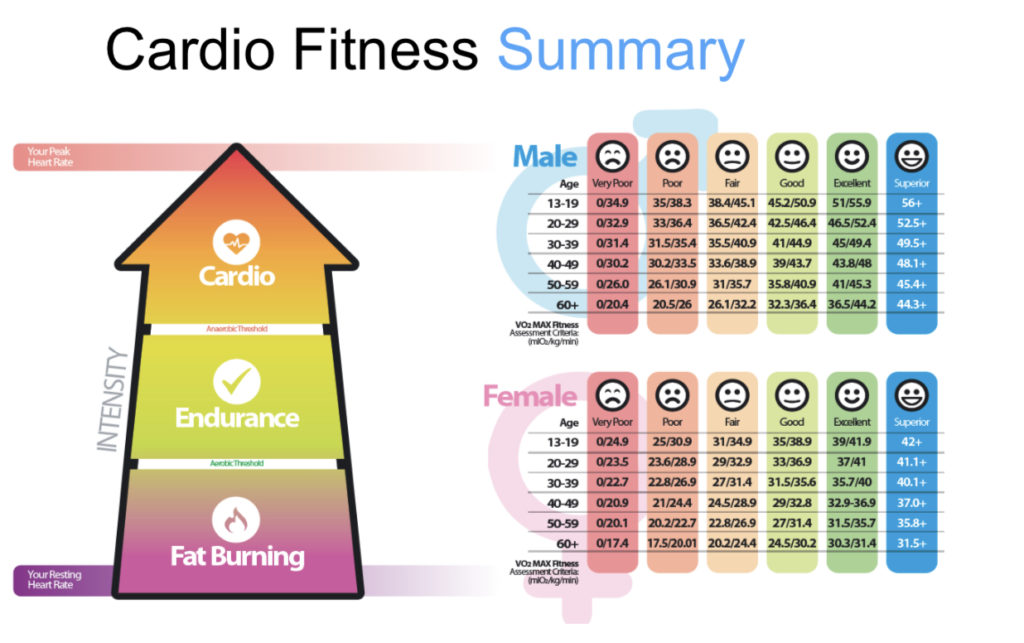
Overall both the treadmill test and the watch estimate provide the same results. The VO2 max accuracy is close enough on either to get to the right general zones to monitor fitness. With the cost of a clinic treadmill test being higher ($49-$149 depending on location) it is more costly to find trends.
A watch does a good enough job to showcase if fitness is improving overall. The clinic treadmill tests are a solid option for an occasionally check-in, and can be used in a similar way that a time trial or a target race is as a way to motivate you during a training cycle.
Overall I was impressed with how close the Apple Vo2 max prediction was to the lab tests. For the most part, based on these observations, the accuracy of the Apple Watch appears good enough to use it as a solid estimate of a true V02 maximum. This assumes that you have done a hard workout and have seen enough consistency in the Apple readings to assume that the results are not a simple outlier.
Since there is not much more that you can do with a more accurate reading, the Vo2 max that Apple health kit provides is sufficient to encourage most behaviors. If for some reason you want to train your body to optimize for this metric it is worth ensuring that you have a good end result in mind that is a proxy for the measurement (improving a 5k running time, feeling better on weekly hill climb bike rides with friends, hiking a few mountains) since it ultimately is only an indicator of fitness and is not something that is routinely looked at as the end all measure of fitness.
Accuracy Of Apple Watch in Other Metrics
VO2 Max is not the only metric where the consistency and accuracy of the measurement matter. Even for things as simple as step tracking will vary depending on the device that you wind up using.
We have previously reviewed the step tracking of Apple Watch, comparing it to Amazon Halo, where the difference in step count can be as high as 25%. When it comes to sleep tracking the Apple Watch accuracy was within 10% of the total sleep time measured by the Amazon Halo as well.
When it comes to other metrics related to wellness, the measurement can be even further off. Comparing body composition types reveals that lab tests can vary by almost 30% when compared to app based images and smart scales.
All this is to say, that when it comes to the accuracy of VO2 max, being within single digits percentage difference from a lab tests means it is a pretty solid estimate.
Great article!
Just a heads-up… it looks like you have the figures reversed for Apple Watch versus Dex.
Cheers
Grant
Thanks Grant! You are right, we had them mixed in one place. We’ve updated this to reflect the right numbers and show that in our analysis Apple Watch series 7 was slightly over estimating VO2 max compared to the lab results.